An analogy
An analogy of a 3 lane highway anywhere in the world, we are not going to discuss the highway location, nor the travelers.
Entry and Exit
We will explain the points of entry and exit, the speed in which we would expect in each lane and how the two directions on any highway tell us.
South
We can assume that our suppliers travel in one direction for the purpose of this analogy we will assume they are in our southbound direction on any of the three lanes.
North
We can assume travelers Northbound on the highway are customers with the revenue outcome measured in any entering traveler. We can assume the revenue was recognized at the exit of the traveler when exiting the highway.
Three lanes
In either direction we can assume the traveler enters the highway in some motor vehicle. We are not concerned about the make, model or color and even less concerned about the driver.
In this analogy we simply know these details exist, which may influence the rate of speed the traveler moves in either North or South directions.
As with any highway, we have a slow lane that all travelers enter the highway by merging into the slow lane. As the traveler accelerates they may move into the middle lane and eventually the farthest lane to the left.
Performance Measures
The performance of an organization can be derived by the number of travelers entering in one direction and how quickly they begin to measure the make and models entering in the North direction after exiting from the South bound direction. We are assuming that south bound relates our suppliers with the build of an offer, exiting implies a customer can pick up the vehicle and travel North as they purchase the vehicle.
Design Strategy
New Business Models
Any entrance and exit isn't restricted by the design, we are predicting the rate of speed the new business models will be traveling slower in the first lane before they are allowed to merge on to the middle or farthest left lane. We suspect they will exit and enter frequently, therefore they will be best suited to travel in the first slow lane.
Advanced Offers - Risk According to the Security Exchange Commission
The middle lane travelers who first enter, then accelerate and merge to the middle lane. They may merge further left to the fast lane with the assumption that they will not impede the faster travelers.
Assume this behavior or design pattern speaks to the way these offers ramp up and come back to get re-aligned several times before making it to the fast lane.
The fast lane-Build Order Transfer models
In some cases the commuter lane, where the distribution model works with a partner to allow the fully sustained model.
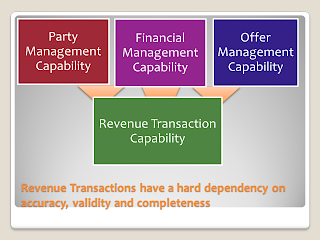
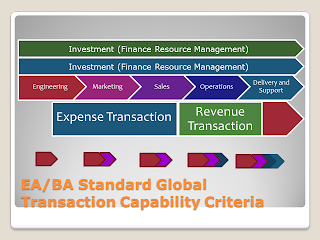
Capabilities
Basically our management capabilities and transaction capabilities are designed for the best and known design patterns. Your organization should be measuring the performance against these criteria for external stakeholders. In doing so you continue with your liberal approach to decision making.
You quickly can recover in cases where you have over-corrected. You are on your way to cloud services in this basic design and ready for new strategies every time. No longer should you have to re-visit the enterprise or business architecture, rather the color, make and model investments are the scope of your future investments.
Don't misunderstand, every road needs to be re-surfaced and new exit and entrances will be required. However, the timelines of acquiring this activity no longer hinders your new business model. Technology can be aligned to this model for faster and better services without customizations every time.